Lactoferrin is a protein contained in the milk and saliva of mammals such as humans. It is known to exhibit various physiological functions such as antimicrobial activity and immunomodulatory action. Among them, it is abundant in breast milk, especially in the first milk, and protects babies with weak resistance from infection by pathogens and viruses. It is considered an important ingredient.
In the discussion of the summary of this report, lactoferrin is infectious by binding to the surface of viruses such as norovirus and rotavirus and the gastrointestinal cells that are the sites of infection, and suppressing the infection of the virus to the gastrointestinal cells. It is said that it is possible that the onset of gastroenteritis was suppressed and the symptoms were alleviated.
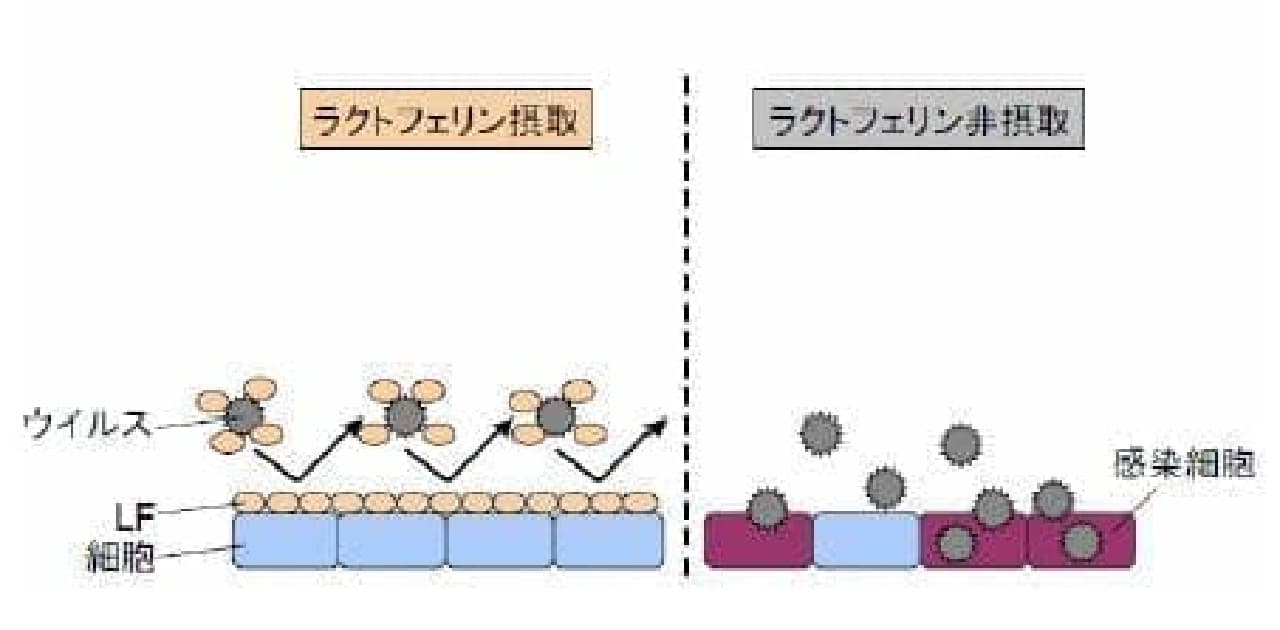
■ [PDF] Report on the effect of lactoferrin on viral infectious gastroenteritis such as norovirus
![[Verification] Eyebrow koala, Monster Hunter rare seal, gold and silver angel, wish pino, chocolate egg, curl secret character ... What is the probability of hitting something you care about !? [Spoiler attention]](https://image.entabe.jp/upload/articles/21124/54a0e931614e7cad2e235c4565ae67cc_special.jpg)











![Lotte "Premium Ghana Whip Selection" Premium Ghana Chocolat Whip [Milk Vanille] and Premium Ghana Chocolat Whip [Douvre Nuts] assortment pack to compare.](https://image.entabe.jp/upload/articles/54356/acc3b61aeb4276b095f3e82e05cde06c_related.jpg)




