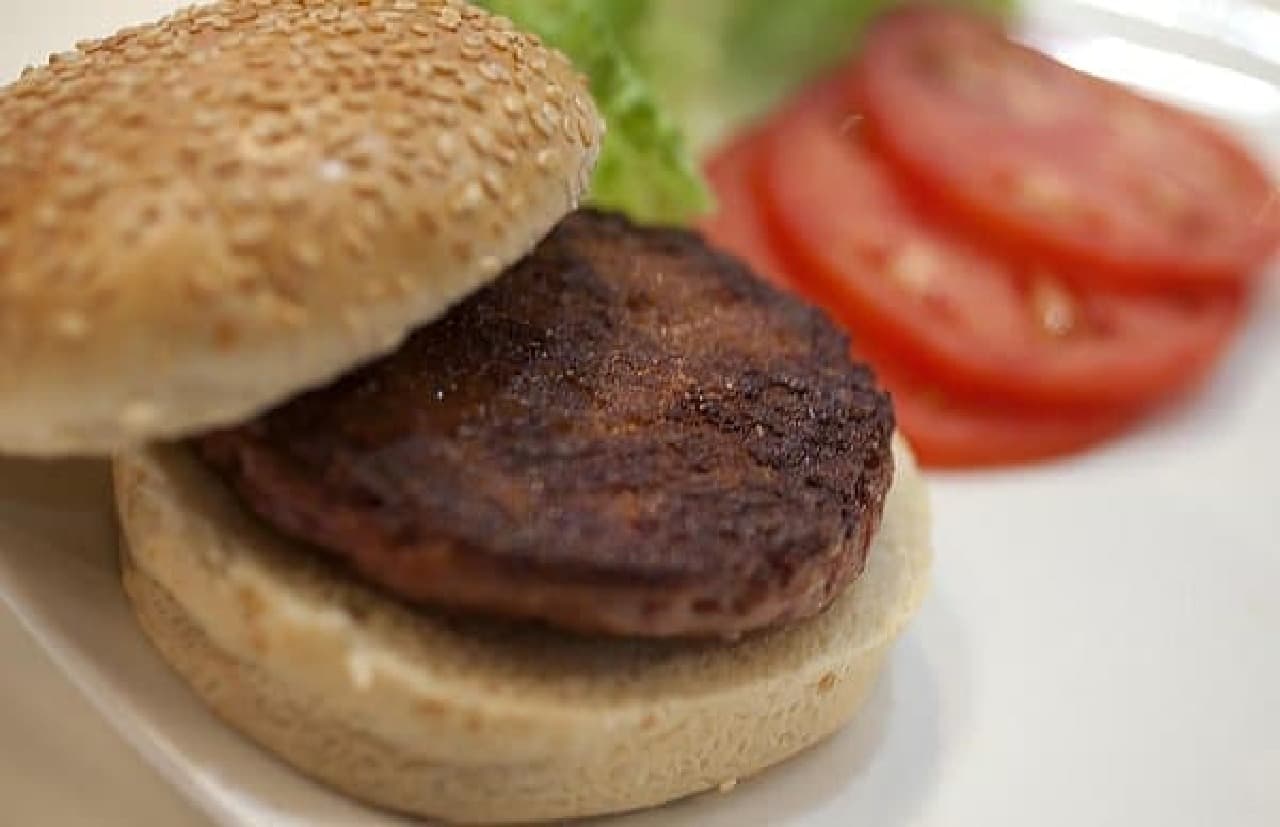

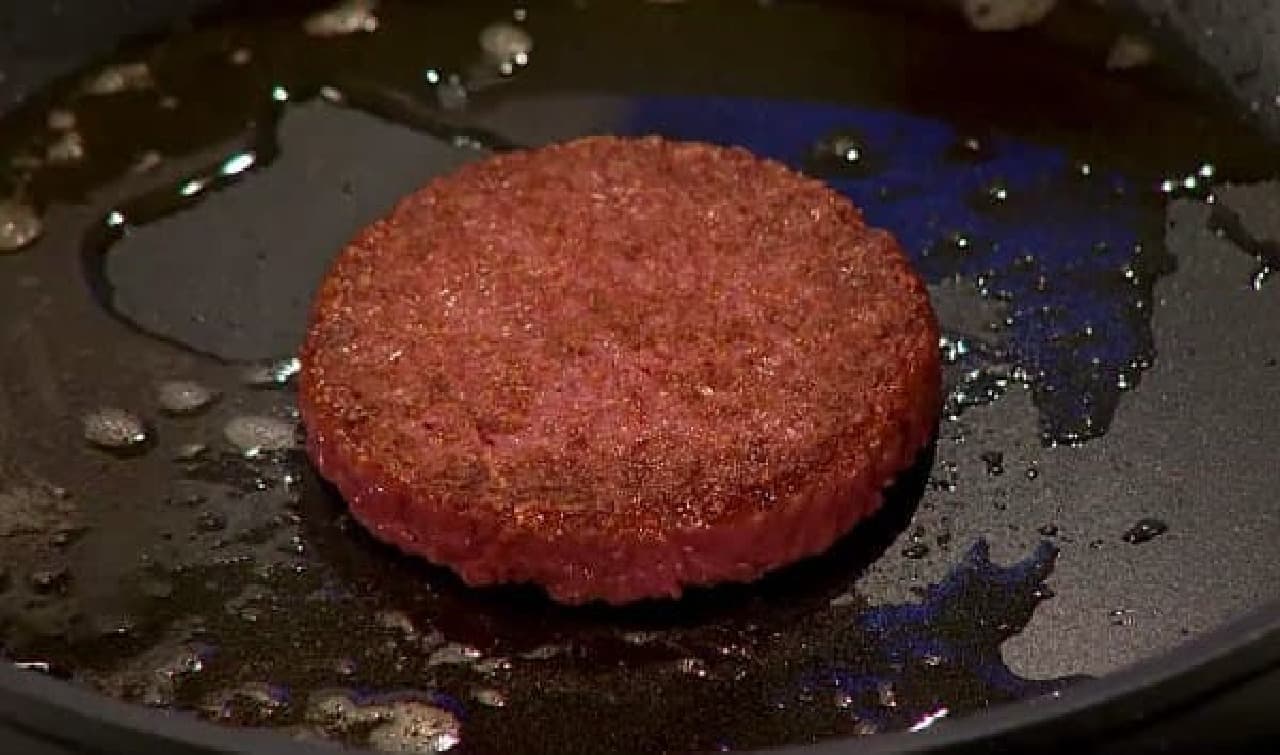
More than 200 journalists and researchers invited to the event witnessed an artificial meat burger being cooked and sampled in front of them.
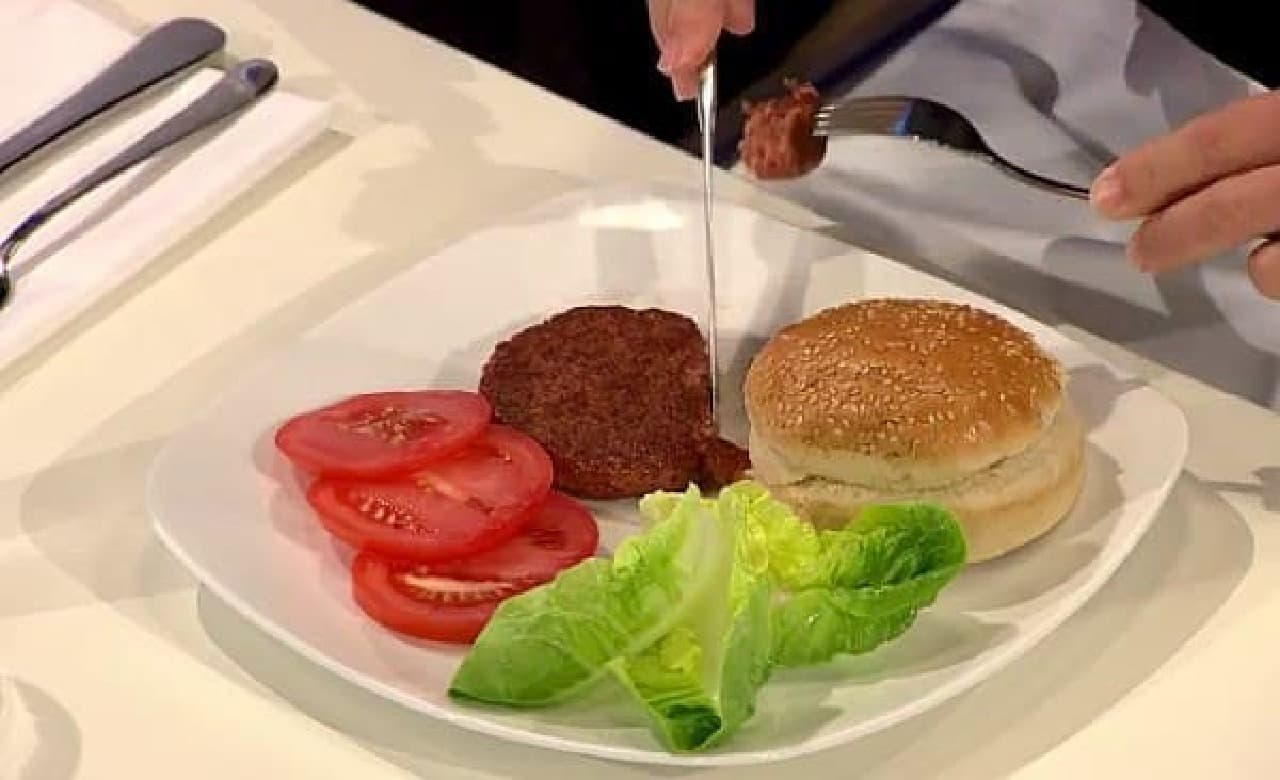

Nutrition researcher Hanni Rutzler, who tasted artificial meat, describes the taste of artificial meat burgers as follows:
"I thought it was softer, but it wasn't. I knew it wasn't fat at all. In terms of taste, I didn't have enough salt and pepper."

Food writer Josh Schonwald said:
"The texture felt like meat. What I lacked was fat. I didn't feel any fat. The moment I chewed, I thought it was a normal hamburger, but I thought it was completely normal. The reason I didn't have it was ketchup. I've been eating burgers for over 20 years, but I've never eaten burgers without ketchup. I also want onions, jalapenos and bacon. "
The hamburger was developed by Mark Post, a professor at Maastricht University in the Netherlands. Mr. Post spent about 32.5 million yen in Japanese yen on the development of this artificial meat hamburger. That's about 100,000 regular hamburgers. The development funding was also provided by Google co-founder Sergey Brin.
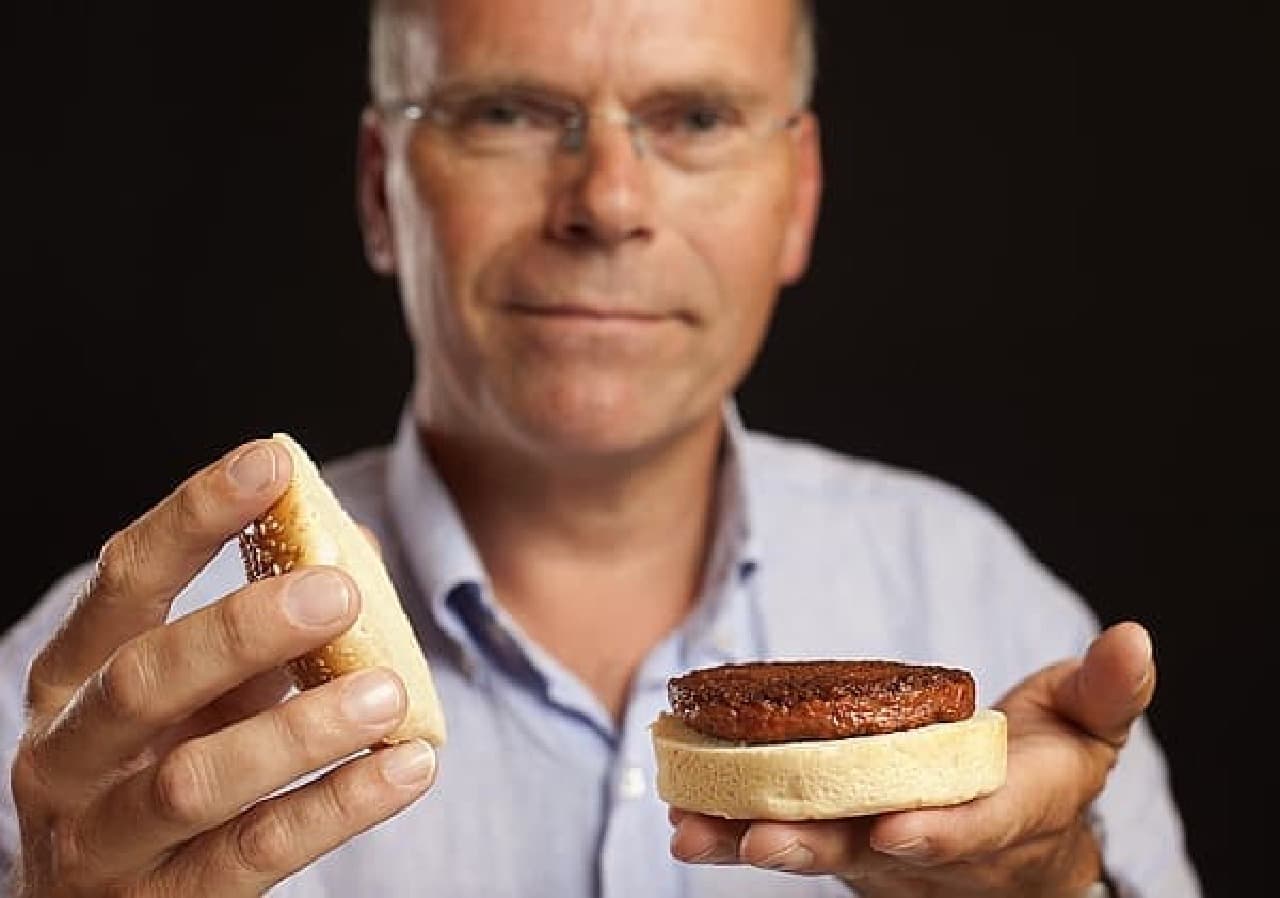

The artificial meat used for the hamburger sampled this time was made by culturing cell tissue collected from cattle. The harvested cells initiate cell division in a Petri dish. It is said that one cell divides up to 1 trillion. The divided cells naturally connect to become myotube cells and grow into muscle fibers.
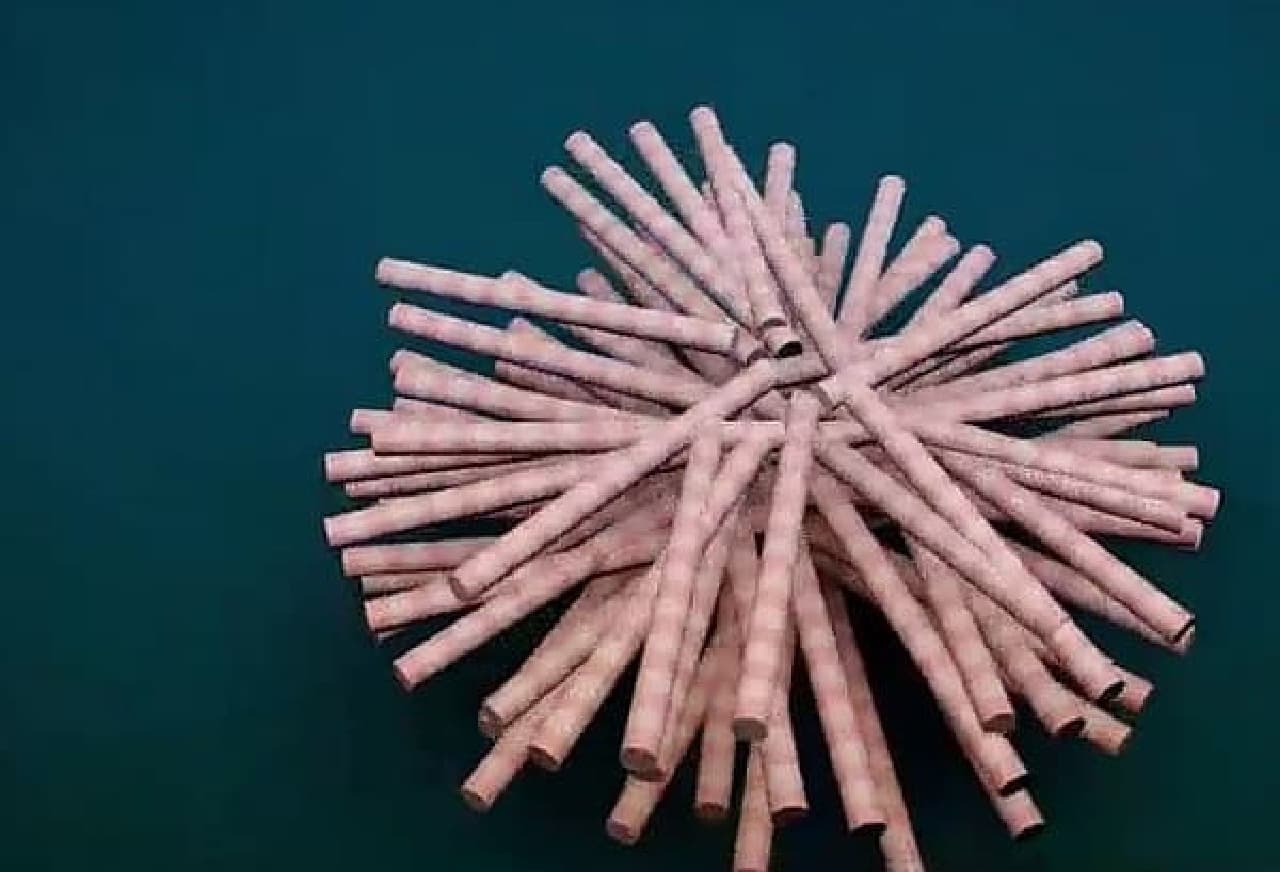



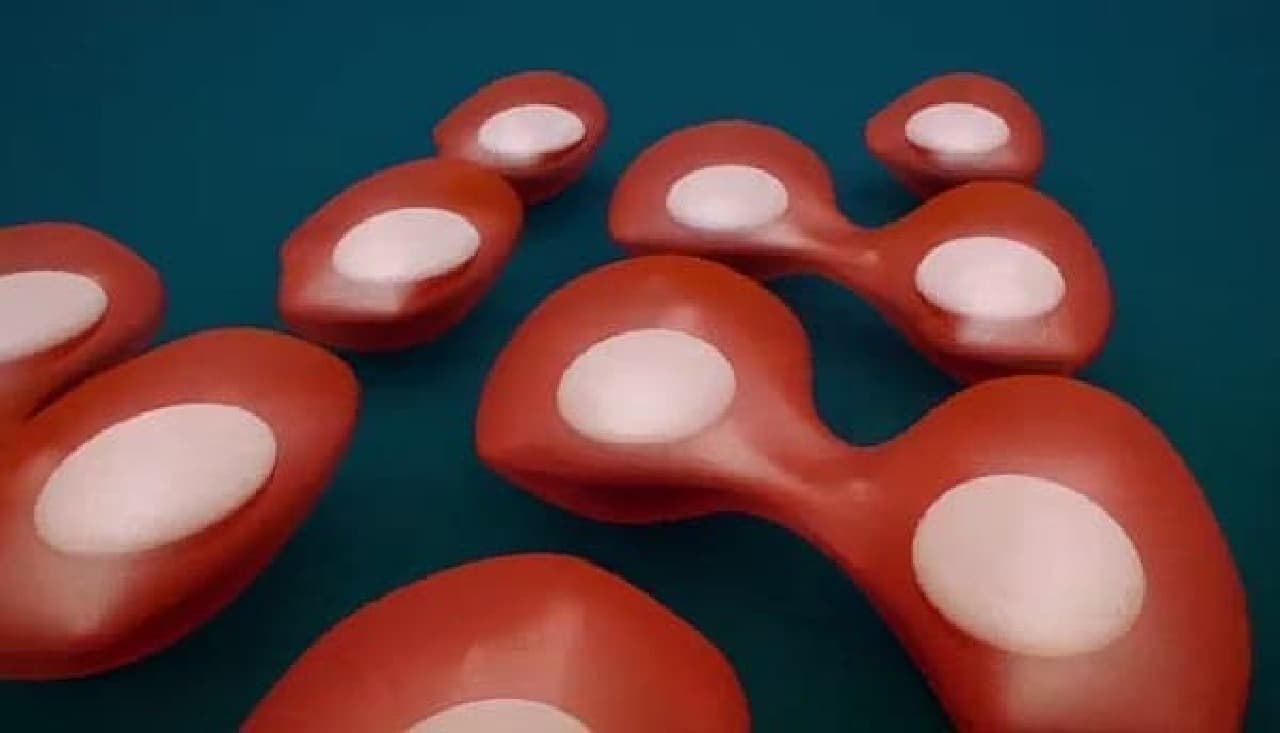
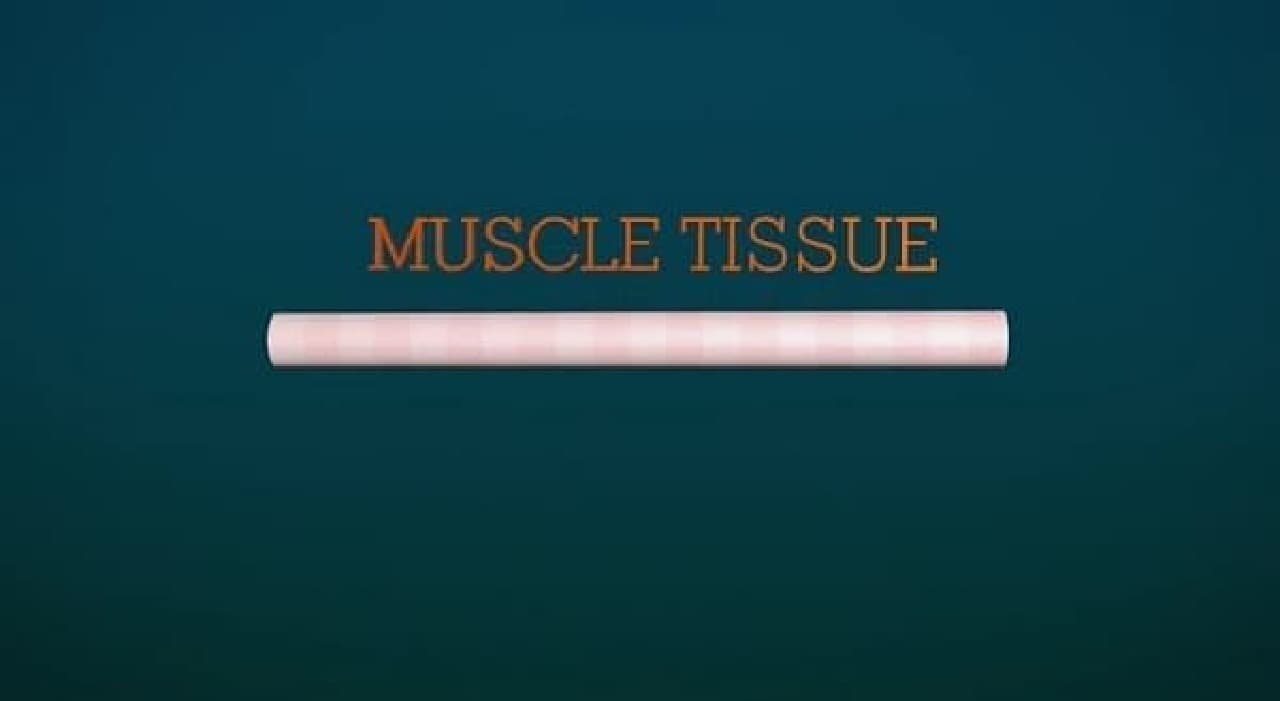

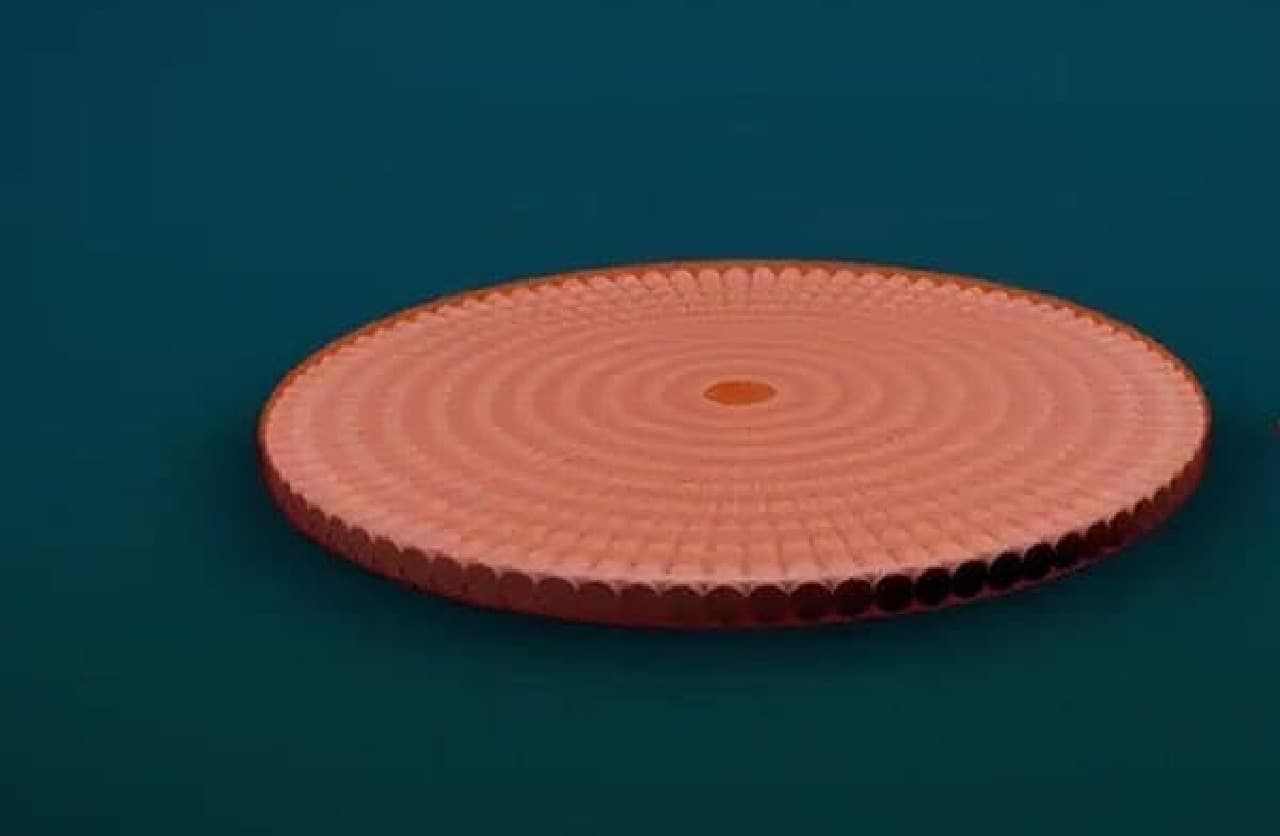

There are no blood vessels that carry nutrients in muscle fibers cultured in the laboratory. For this reason, it is said that cells were artificially nourished during the growth process of muscle tissue. Also, unlike real cows, artificial meat does not exercise voluntarily. For this reason, it is said that stretching and micro-exercise were also applied to the artificial meat so that the muscles would not weaken. In addition, artificial meat does not have the red color of real beef because it does not contain blood. For this reason, the artificial meat is said to have been colored with red turnip juice.
This artificial meat burger patty is made by adding a binder to the artificial meat of 20,000 muscle fibers made in this way.
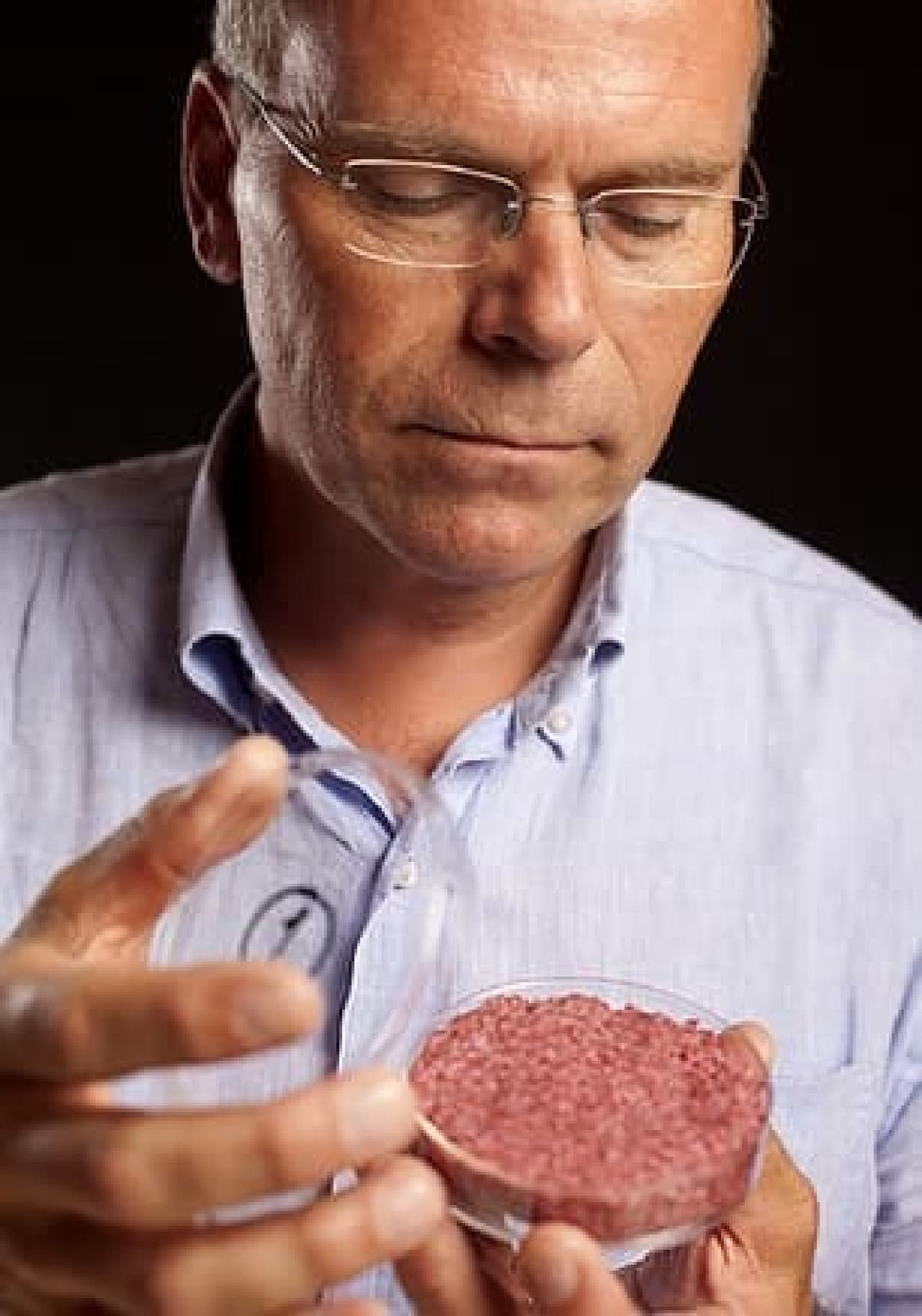

Post states that the development of artificial meat offers a number of benefits. For example, 18% of the carbon dioxide that causes global warming is emitted by cattle breeding, Post said. Post argues that if artificial meat is put into practical use and the number of cattle raised can be reduced, it will also help stop global warming.









![[2023 Latest] Summary of "mornings" for seven hamburger chains! McDonald's, Moss, Lotteria, Fast Kitchen, Wendy's, Freshness, Becks](https://image.entabe.jp/upload/articles/55581/7afa165e62e2241b800e4fdfcc2717e5_special.jpg)








